Organizations are increasingly turning to Project Portfolio Management (PPM) as a strategic approach to ensure that their projects align with overarching business objectives. PPM not only helps prioritize projects but also optimizes resource allocation, mitigates risks, and maximizes the value derived from investments. As organizations strive for operational excellence, understanding the latest strategies, trends, and best practices in PPM becomes imperative.
Understanding Project Portfolio Management
Project Portfolio Management is the centralized management of processes, methods, and technologies used by project managers and project management offices to analyze and collectively manage current or proposed projects based on numerous key characteristics. The goal is to determine the optimal mix and sequencing of proposed projects to best achieve the organization’s overall goals.
Key Components of PPM
- Project Selection: Choosing the right projects based on strategic alignment, potential return on investment, and resource availability.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently assigning resources to projects based on priority and capacity.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously assessing the progress and performance of projects to ensure alignment with strategic goals.
- Risk Management: Identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks across the portfolio to safeguard the organization’s investments.
Strategies for Optimizing PPM
1. Align Projects with Organizational Strategy
One of the primary strategies for optimizing PPM is ensuring that every project aligns with the organization’s strategic goals. This involves developing a clear understanding of the organization’s vision, mission, and objectives. A robust project selection framework that evaluates potential projects against these criteria can help prioritize initiatives that contribute most significantly to strategic outcomes.
2. Implement a Scoring Model
Utilizing a scoring model can facilitate objective decision-making when it comes to project selection. By creating a scoring system that evaluates projects based on criteria such as financial benefits, strategic alignment, risk, and resource requirements, organizations can systematically compare and prioritize projects. This approach minimizes bias and ensures that the most valuable projects are selected for execution.
3. Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective PPM requires collaboration across various departments and functions. By fostering a culture of teamwork and communication, organizations can leverage diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to better decision-making and project outcomes. Regular cross-functional meetings and updates can help maintain alignment and ensure that all stakeholders are informed and engaged.
4. Utilize Technology and Tools
Investing in PPM software and tools can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of project portfolio management. Modern PPM tools offer features such as real-time dashboards, reporting capabilities, and resource management functionalities. These tools enable organizations to track project performance, manage resources, and visualize portfolio health, allowing for informed decision-making.
5. Emphasize Continuous Improvement
Organizations should adopt a mindset of continuous improvement within their PPM processes. Regularly reviewing and refining project selection criteria, resource allocation strategies, and performance metrics can help identify areas for enhancement. Gathering feedback from project teams and stakeholders can also provide valuable insights into what works well and what needs adjustment.
6. Focus on Benefits Realization
Maximizing value from projects goes beyond merely completing them on time and within budget. Organizations should focus on benefits realization by establishing clear metrics for success and tracking the actual benefits delivered post-project completion. This approach not only validates the project’s value but also informs future project selection and prioritization.
7. Manage Risks Proactively
Risk management is a critical component of PPM. Organizations should develop a risk management framework that identifies potential risks at the portfolio level. By assessing the impact and likelihood of risks, teams can implement mitigation strategies early on, reducing the likelihood of negative impacts on project outcomes.
Trends in Project Portfolio Management
As PPM continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of project management:
- Agile and Hybrid Methodologies: The adoption of Agile and Hybrid practices such as ROPE, within PPM allows organizations to respond to changes more swiftly and adapt to evolving market conditions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging data analytics to inform project selection and performance monitoring is becoming increasingly important as organizations seek to make informed decisions based on empirical evidence.
- Sustainability Focus: Organizations are beginning to prioritize projects that contribute to sustainability and corporate social responsibility, aligning with broader societal goals.
Conclusion
Optimizing Project Portfolio Management is essential for organizations looking to maximize value and achieve strategic success. By aligning projects with organizational goals, implementing effective selection and scoring models, fostering collaboration, leveraging technology, and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can enhance their PPM practices. As trends like Agile methodologies and data-driven decision-making continue to emerge, staying informed and adaptable will be crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in an ever-changing business landscape. Embracing these strategies will not only improve project outcomes but also drive long-term organizational success.
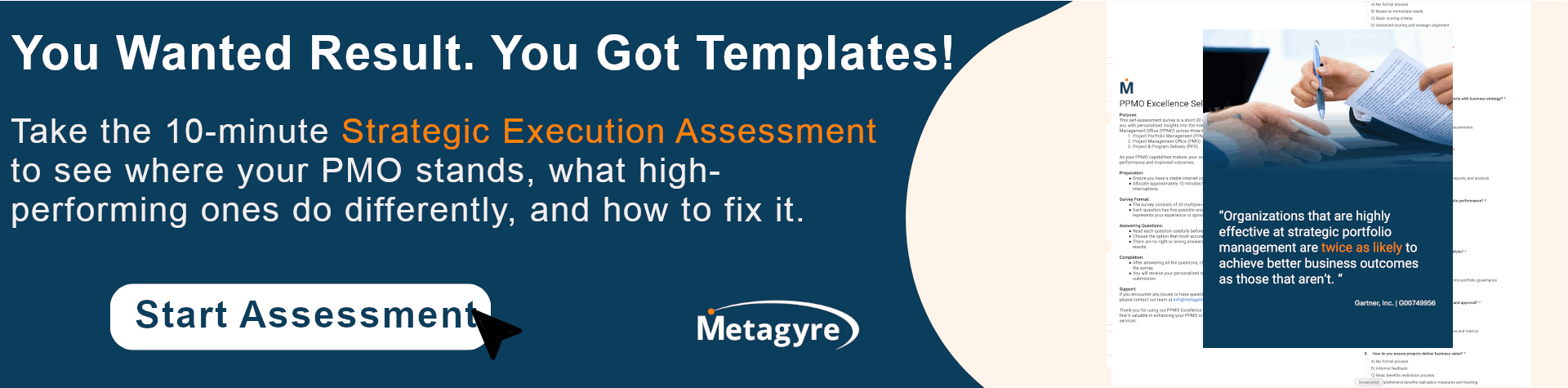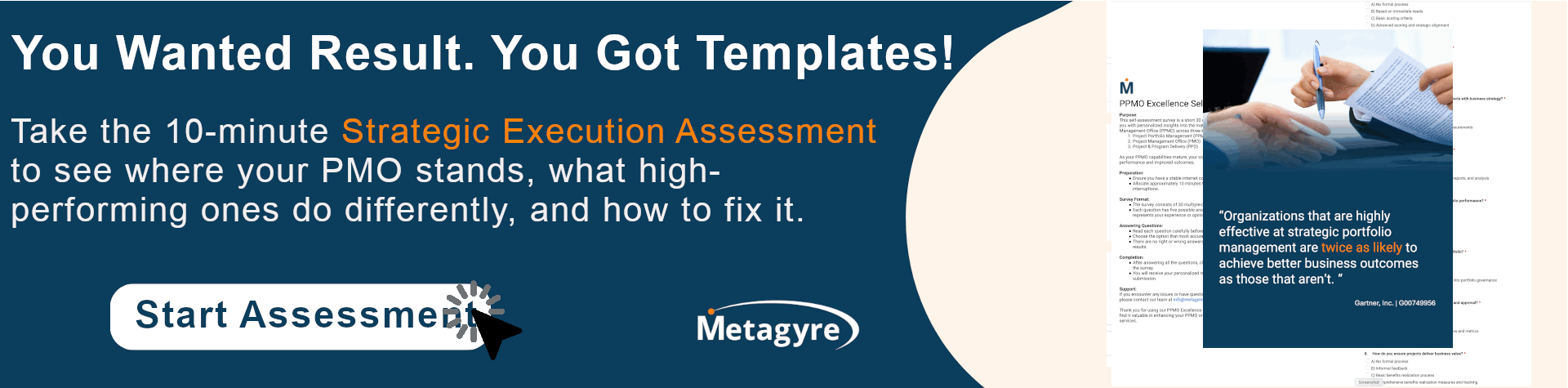
















One thought on “Optimizing Project Portfolio Management: Strategies for Maximizing Value and Organizational Success”
Comments are closed.